| 1PEGylated vs. Native Proteins |
|---|
Applications
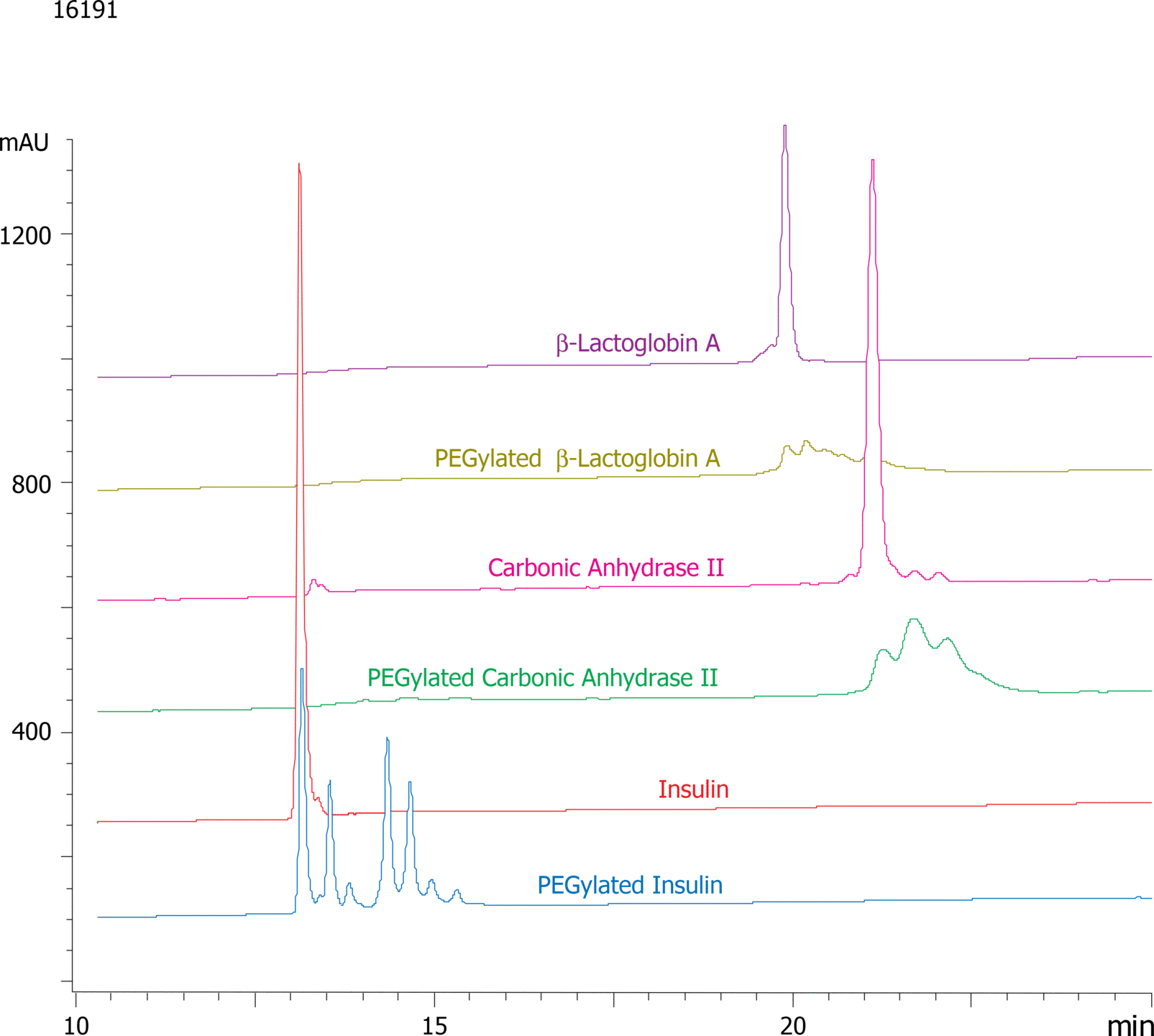
Overlay of PEGylated vs. Native Proteins on Jupiter® 300 C4 Column
16191
Separation Mode: Reversed Phase
Reversed Phase
C4
HPLC
Pharmaceutical/Biopharmaceutical
Life Science
Protein
Biochemical Compound / Nutrient
Analytes
Details
LC Conditions (App ID: 16191)
Column: |
Brand Name: Jupiter |
Part No: |
Phase Name: C4 |
Sample Note: Application Focus: Using Jupiter 300 C4 for purifying PEGylated proteins.
For many protein therapeutics, a polyethylene glycol (PEG) group is attached to a protein to increase its serum half-life. This addition of such PEG groups to a protein complicates both the characterization and purification of such PEG/protein conjugates away from the "non-PEGylated" protein species. This application is show the utility of reversed phase chromatography for purifying PEGylated proteins. Different protein solutions in PBS (pH 7.4) was reacted with an excess of the PEGylation reagent dissolved in DMSO (Methyl-PEO12-NHS Ester) and incubated in an ice bucket for up to two hours Reaction mixture was quenched with an equal volume of 50 mM Tris/1 % trifluoroacetic acid (TFA) (pH~2).
As mentioned in App ID# 16198, the PEGylation reaction concurrently occurs rapidly at several different protein sites in a fixed ratio. In every protein tested there was always more than one PEGylated protein peak observed by reversed phase HPLC; each seemingly ascribed to a different site of PEG modification. Unlike gel filtration which only separates PEGylated proteins by degree of modification, it appears that protein modification site influences the reversed phase separation of proteins much more than the degree of modification; such results show the utility of using reversed phase chromatography for purifying and analyzing various PEGylated proteins. |
Similar Applications
No Data