Reversed Phase HPLC
Reversed-phase Liquid Chromatography (RP-LC)
Being the most common principle of HPLC/UHPLC separation mode, reversed-phase chromatography offers dynamic retention of compounds with hydrophobic and organic functionality. Retention of these compounds by reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) involves a combination of hydrophobic and van der Waals-type interactions between each target compound and both the stationary phase and mobile phase.
A reversed-phase HPLC column is a type of chromatography column commonly used in analytical chemistry for separating compounds in a mixture. It is a specific type of stationary phase used in HPLC, where the stationary phase is non-polar (hydrophobic), and the mobile phase is polar.
Stationary phases used in reversed-phase chromatography typically consist of varying lengths of hydrocarbons such as C18, C8, and C4 or strongly hydrophobic polymers such as styrene divinylbenzene.
- The most common type of reversed-phase HPLC Column is the C18 column. It is the most preferred as it offers an excellent range of hydrophobic separation power along with high surface area coverage.
- C8 HPLC columns are used when less retention compared to a C18 is needed.
- C4 and C5 HPLC columns are commonly used to separate large macromolecules such as proteins.
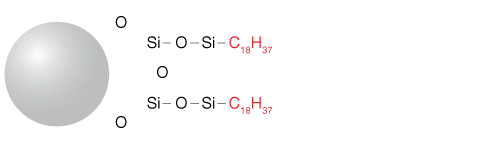
How Does Reversed-Phase HPLC Work?
Reversed-phase HPLC separates molecules based on their hydrophobicity. In this process, solute molecules interact with hydrophobic ligands immobilized on the stationary phase (sorbent). Initially, the sample is introduced under aqueous conditions, allowing solutes to bind to the sorbent.
Elution occurs either under isocratic conditions, where the organic solvent concentration remains constant throughout the run, or under gradient conditions, where the concentration of organic solvent increases stepwise or continuously over time. As a result, solutes are eluted in order of increasing hydrophobicity.
Stationary Phase
The stationary phase consists of hydrophobic materials chemically bonded to porous silica particles. Common bonded hydrocarbons include C18 (octadecylsilane), C8, or C4 chains, with C18 being the most prevalent. The retention of compounds increases with the length of these hydrocarbon chains—longer chains (e.g., C18) retain hydrophobic molecules more effectively than shorter ones (e.g., C8).
Mobile Phase
The mobile phase is polar, typically a mix of water and organic solvents like methanol or acetonitrile. A gradient elution is often employed, starting with a high-water content (polar) and gradually increasing the organic solvent proportion to reduce polarity. This allows less hydrophobic compounds to elute first, followed by more hydrophobic ones. Additives such as buffers adjust pH, influencing solute ionization and retention.
Retention Mechanism
Separation occurs through partitioning between the hydrophobic stationary phase and polar mobile phase:
- Hydrophobic interactions: Non-polar compounds adsorb strongly to the stationary phase, while hydrophilic ones elute quickly.
- Gradient elution: Increasing organic solvent concentration disrupts these interactions, selectively eluting compounds based on hydrophobicity.
- Molecular simulations reveal that C18 chains adopt flexible conformations, creating a dynamic interface where solutes partition based on their affinity for the hydrophobic chains versus the mobile phase.
Applications of Reversed-phase Chromatography
Reversed-phase chromatography is a subtype of HPLC and is widely used for separating and analyzing a variety of compounds. Reversed-phase chromatography is used across various fields:
- Pharmaceutical Analysis: Reversed-phase chromatography is used to determine the purity and potency of drug substances and products and to evaluate their stability. It's also used in the analytical separation of drugs and their metabolites.
- Environmental Testing Reversed-phase chromatography helps detect and measure pollutants like pesticides, herbicides, and volatile organic compounds.
- Biochemical Research: Reversed-phase chromatography is effective for separating proteins, peptides, and nucleic acids. It can also allow for differential separation of the proteome.
- Food and Beverage Analysis: Reversed-phase chromatography is employed to identify and quantify vitamins, sugars and carbohydrates, organic acids and amino acids.
- Metabolomics: Comprehensive analysis of metabolites and identification of biomarkers. Reversed-phase HPLC columns facilitate the thorough analysis of metabolites and the discovery of biomarkers, which are essential for diagnosing diseases and developing new drugs.
How to Choose Reversed-Phase HPLC Columns?
Selecting the right Reversed-phase HPLC column is essential for achieving optimal separation, efficiency, and resolution. The key factors to consider include solid support type and column selectivity based on analyte characteristics.
Choosing the Right Solid Support
The morphology of the stationary phase significantly impacts column performance. Common solid supports include:
- Core-Shell & Organo-Silica Core-Shell
- Features a solid silica core with a porous shell.
- Provides faster chromatography and higher efficiency than fully porous particles.
- Ideal for method transfers between laboratories.
- Fully Porous Thermally Modified Silica
- High efficiency, robustness, and versatility.
- Suitable for UHPLC, HPLC, and preparative HPLC applications.
- Traditional Fully Porous Silica
- Offers excellent mechanical strength.
- Best for scaling up from analytical to preparative/process applications.
- Fully Porous-Organo Silica
- Contains organic groups, enhancing resistance to dissolution at high pH.
- Extends column longevity under extreme conditions.
Column Selectivity & Its Impact on Separation
Column selectivity is the most influential factor in achieving high resolution. It is characterized using the hydrophobic subtraction model, which considers:
- Hydrophobicity: Dominant for neutral compounds.
- Steric Influences: Affects shape selectivity and solute accessibility.
- Hydrogen Bonding
- Donating Capacity: Enhances retention of hydroxyl/amine-containing compounds.
- Accepting Capacity: Affects interaction with hydrogen bond donors.
- Cation Selectivity
- At Neutral pH: Influences ionized bases.
- At Low pH: Plays a role in retention behavior.
Matching Column Selectivity to Analyte Classes
Different analytes require specific selectivity profiles to ensure effective separation:
- Hydrocarbon/Hydrophobic Compounds
- High hydrophobicity (e.g., C18) enhances retention.
- Alternative chemistries may be needed to shorten run times without compromising separation.
- Isomers & Isobaric Compounds
- Require columns with multiple interaction mechanisms (e.g., F5 – Pentafluorophenyl).
- Compounds with Hydroxyl or Amine Groups
- Benefit from columns with high hydrogen bond capacity.
- Aromatic/Ring-Containing Compounds
- Require pi–pi interactions for enhanced retention and resolution.
- Polar Acidic Compounds, Non-Ionized Bases, Oxygen- or Halogen-Containing Compounds
- Need specific hydrogen bond donating capacities and cation selectivity for proper retention and separation.