Chiral HPLC
Chiral column chromatography refers to the separation of enantiomers using a chiral HPLC column, an HPLC column that is packed with a chiral stationary phase (CSP). Enantiomers are separated based on the number and type of each interaction that occurs during their exposure to the chiral stationary phase. Some chiral stationary phases (CSPs) can separate a wide range of chiral compounds, while others are useful only for specific types of chiral compounds.
Normal phase solvents are commonly used for chiral HPLC separations; however, reversed-phase solvents can also be used with certain types of chiral stationary phases. Approximately 60% of all pharmaceutical drugs are chiral. Common chiral stationary phases used for chiral HPLC columns are polysaccharide, ligand exchange, protein, helical polymers, macrocyclic, and Pirkle-brush concept.
Chiral separations are essential in industries such as pharmaceuticals, biotechnology, and natural products chemistry, where the accurate identification and purification of optically active compounds are critical. Chiral drugs require highly selective and sensitive analytical methods to ensure their safety and efficacy. Increasingly stringent government regulations are intensifying the demand for rapid, precise, and reproducible techniques to analyze and purify enantiomeric compounds.
In response to these challenges, Phenomenex’s chiral HPLC columns provide an exceptional solution, offering a unique combination of selectivity and versatility for both trace-level analysis and laboratory-scale drug purification.
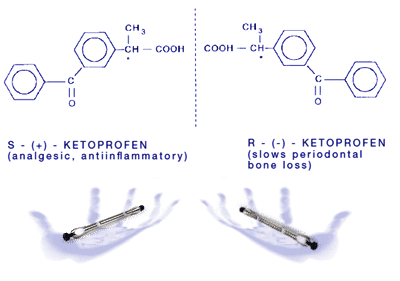
Phenomenex Chiral Chromatography Columns
Phenomenex offers a comprehensive range of cutting-edge chiral columns, recognized as one of the most widely used chiral columns globally. Because with 12 distinct stationary phases, these robust chiral columns are engineered for the direct and indirect separation of a wide range of enantiomeric compounds, such as amines, alcohols, carboxylic acids, hydroxy acids, amino acids, ketones, lactones, ethers, esters, and other biologically active substances.
As a leader in advanced chiral separations, Phenomenex offers an unparalleled range of products designed to meet the diverse demands of industries requiring precise chiral analysis. Supported by a specialized chiral separation services laboratory, Phenomenex provides expert guidance in column selection, method development,, and every facet of chiral chromatography. Whether researchers are creating new methods or optimizing existing ones, Phenomenex's dedication to innovation and expertise guarantees exceptional performance and reliability in chiral separations.